Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
; ; Yamazaki, Toshihiko; ; ; Kondo, Toshinari*; *
JNC TN8400 2001-030, 99 Pages, 2002/01
There is a great deal of that we build a Base-Isolated building with the quaternary deposit ground. In an atomic energy institution, a study request is strong. When we build a Base-Isolated building with the quaternary deposit ground, evaluation of earthquake vibration of a vertical direction is an important problem. In an atomic energy institution, we design it by big earthquake load, and therefore examination is necessary. And, in this study, we do examination to build a Base-Isolated building with the quaternary deposit ground, we report it about an evaluation method of a design. Furthermore, we report that we estimated pipe laying and machinery to put in a building of Base-lsolated.
Kurihara, Ryoichi; Ajima, Toshio*; Ueda, Shuzo; Seki, Yasushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 38(7), p.571 - 576, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; Ohno, Shuji;
JNC TN2400 2000-006, 56 Pages, 2000/12
Sodium combustion analyses were performed using ASSCOPS version 2.1 in order to obtain background data for evaluating the validity of the mitigation system against secondary sodium leak of MONJU. The calculated results are summarized as follows. (1)Peak atmospheric pressure  4.3 kPa[gage] (2)Peak floor liner temperature
4.3 kPa[gage] (2)Peak floor liner temperature  870
870 C, Maximum thinning of liner
C, Maximum thinning of liner  2.6mm (3)Peak hydrogen concentration <2% (4)Peak floor liner temperature in the spilt sodium storage eell
2.6mm (3)Peak hydrogen concentration <2% (4)Peak floor liner temperature in the spilt sodium storage eell  400
400 C , Peak floor concrete temperature in the spilt sodium storage cell
C , Peak floor concrete temperature in the spilt sodium storage cell  140
140 C.
C.
Sugino, Kazuteru; Iwai, Takehiko*;
JNC TN9400 2000-098, 182 Pages, 2000/07
In order to support the Russian excess weapons plutonium disposition, the international collaboration has been started between Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) and Russian Institute of Physics and Power Engineering (IPPE). In the frame of the collaboration, JNC has carried out analyses on the BFS-62 assemblies that are constructed in the fast reactor critical experimental facility BFS-2 of IPPE. This report summarizes an experimental analysis on the BFS-62-1 assembly, which is the first core of the BFS-62 series. The core contains the enriched U0 fuel surrounded by the U0
fuel surrounded by the U0 blanket. The standard analytical method for fast reactors has been applied, which was used for the JUPITER and other experimental analyses. Due to the lack of the analytical data the 2D RZ core calculation was mainly used. The 3D XYZ core calculation was applied only for the preliminary evaluation. Further in terms of the utilization of the BFS experimental analysis data for the standard data base for FBR core design, consistency evaluation with JUPITER experimental analysis data has been performed using the cross-section adjustment method. As the result of analyses, good agreement was obtained between calculations and experiments for the criticality and the reaction rate ratio. However, it was found that accurate evaluation of the reaction rate distribution was impossible without exact consideration of the arrangement of the two types of sodium (with and without hydrogen impurity), which can be accommodated by the 3D core analysis, thus it was essentia1. In addition, it was clarifie that there was a room for an improvement of the result on the reaction rate distribution in the blanket and shielding regions. The application of the 3D core calculation improved the result on the control rod worth because 3D core model can more exactly consider the shape of the control rod. Furthermore it was judged that the result of the analysis on the sodium void reactivity .....
blanket. The standard analytical method for fast reactors has been applied, which was used for the JUPITER and other experimental analyses. Due to the lack of the analytical data the 2D RZ core calculation was mainly used. The 3D XYZ core calculation was applied only for the preliminary evaluation. Further in terms of the utilization of the BFS experimental analysis data for the standard data base for FBR core design, consistency evaluation with JUPITER experimental analysis data has been performed using the cross-section adjustment method. As the result of analyses, good agreement was obtained between calculations and experiments for the criticality and the reaction rate ratio. However, it was found that accurate evaluation of the reaction rate distribution was impossible without exact consideration of the arrangement of the two types of sodium (with and without hydrogen impurity), which can be accommodated by the 3D core analysis, thus it was essentia1. In addition, it was clarifie that there was a room for an improvement of the result on the reaction rate distribution in the blanket and shielding regions. The application of the 3D core calculation improved the result on the control rod worth because 3D core model can more exactly consider the shape of the control rod. Furthermore it was judged that the result of the analysis on the sodium void reactivity .....
JNC TN4400 2000-002, 33 Pages, 2000/06
An on-site plant analyzer can provide analysis support in evaluating plant dynamic characteristics when unplanned events occur in a nuclear power station. The plant analyzer contains a plant-dynamics analysis code, which efficiently and quickly analyzes the plant dynamic characteristics. Elements being developed for the on-site plant analyzer include utilities to build plant models for performing analyses and to retrieve plant operation data. The addition of these elements to the analysis code supports the plant-dynamics analysis works in MONJU, in particular, to assist the analyses of start up tests. The system contains the FBR plant-dynamics analysis code "Super-COPD", which is based on the "COPD" code that was used in the safety licensing of MONJU. One feature of the system is that all operations, e.g., assembling plant models for analysis, are prepared using a GUI (Graphical user Interface). In addition to this feature, the system is able to retrieve directly on- and off-line plant data from MIDAS, the Monju Integrated Data Acquisition System. These plant data are used to supply time-dependent boundary conditions for the plant analysis models. For this report, two case studies were performed. First, the analysis result of a turbine trip test at 40% power operation using the full plant model is described. For the second, performance of the IHX model was evaluated using retrieved plant data for boundary conditions. With the development of this system, improvement in the efficiency of analyses of MONJU start-up tests is expected.
Tozawa, Katsuhiro; ; Kakehi, Isao
JNC TN9400 2000-052, 110 Pages, 2000/04
This report describes accomplishment of development of a cathode processor calculation code to simulate the mass and heat transfer phenomena with the distillation process and development of an analytical model for cooling behavior of the pyrochemical process cell on personal computers. The pyrochemical process using molten salt electrorefining would introduce new technologies for new fuels of particle oxide, particle nitride and metallic fuels. The cathode processor calculation code with distillation process was developed. A code validation calculation has been conducted on the basis of the benchmark problem for natural convection in a square cavity. Results by using the present code agreed well for the velocity-temperature fields, the maximum velocity and its location with the benchmark solution published in a paper. The functions have been added to advance the reality in simulation and to increase the efficiency in utilization. The test run has been conducted using the code with the above modification for an axisymmetric enclosed vessel simulating a cathode processor, and the capability of the distillation process simulation with the code has been confirmed. An analytical model for cooling behavior of the pyrochemical process cell was developed. The analytical model was selected by comparing benchmark analysis with detailed analysis on engineering workstation. Flow and temperature distributions were confirmed by the result of steady state analysis. In the result of transient cooling analysis, an initial transient peak of temperature occurred at balanced heat condition in the steady-state analysis. Final gas temperature distribution was dependent on gas circulation flow in transient condition. Then there were different final gas temperature distributions on the basis of the result of steady-state analysis. This phenomenon has a potential for it's own metastable condition. Therefore it was necessary to design gas cooling flow pattern without ...
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; *; Okano, Yasushi; *; Yamaguchi, Akira
JNC TY9400 2000-012, 91 Pages, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
JNC TN9400 2000-021, 104 Pages, 2000/03
ln this report, research works performed in the Structura1 Safety Engineering Group of OEC/JNC are summarized as the final report of the doctoral fellowship. The main objective of this study is for the enhancement of the nondestructive evaluation techniques for structural components of both magnetic and nonmagnetic material. Studies in three topics have been carried out aiming at the quantitative evaluation of crack with the eddy current testing and the validation of a natural magnetic field based NDE method for detecting mechanical damages in a paramagnetic material. ln the first part of the study, an approach to the reconstruction of the natural crack was proposed and implemented with an idealized crack model for its validation. ln the second part, the correlation of the natural magnetization and the mechanical damages in the SUS304 stainless steel was investigated by using an experimental approach. ln part 3, an inverse method of the measured magnetic fields is proposed for the reconstruction of magnetic charges in the inspected material by using an optimization method and wavalet. As the first work, an approach to the reconstruction of an idealized natural crack of non-vanishing conductivity is proposed with use of signals of eddy current testing. Two numerical models are introduced at first for modeling the natural crack in order to represented it with a set of crack parameters. A method for the rapid prediction of the eddy current testing signals coming from these idealized cracks is given then by extending a knowledge based fast forward solver to the case of a non-vanishing conductivity. Based on this fast forward solver, the inverse algorithm of conjugate gradient method is updated to identify the crack parameters. Several examples are presented finally as a validation of the proposed strategy. The results show that both the two numerical models can give reasonable reconstruction results for signal of low noise. The model concerning the touch of ...
*; Takemura, Morio*
JNC TJ9440 2000-005, 157 Pages, 2000/03
With use of the two-dimensional discrete ordinates code DORT and the standard groupwise shielding design library JSSTDL produced from the latest evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-3.2, experimental analyses for the representative configurations in the Radial Shield Attenuation Experiment of the JASPER were performed. The results were compared with those obtained with use of traditional method DOT3.5/JSDJ2 for the previous JASPER experimetal analyses. In general, the change of the cross section library gives higher results and the change of the transport code gives lower results. Finally the new analysis method gives better agreement with the experimental results and also less deviations of calculational errors between various detectors. Experimental analyses for the thick concrete configulation in the Gap Streaming Experiment of the JASPER was also performed with the new analysis method, after solving the poor agreement found in last year with the original JASPER experimental analyses. The same tendency due to the library change was confirmed with the above mentioned analyses of the Radial Shield Attenuation Experiment. Compilation of the input data necessary for future reanalyses of important configurations in JASPER experiments were continued through the above-mentioned experimental analyses and related informations were added for repletion of the database preserved in a computer disk holding previously accumulated data. Input data descriptions were made for auxiliary routines needed for the experimental analyses and their sample data were compiled and stored in the database.
Mori, Koji*; Neyama, Atsushi*; Nakagawa, Koichi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-064, 175 Pages, 2000/03
In this study, the following tasks have been performed in order to evaluate the stability of earthquake resistance for the engineered barrier system(EBS) of High Level Waste (HLW) geological isolation system. (1)validation studies for the liquefaction model. The function of single-phase analysis without interaction between soil and pore water in three-dimensional effective stress analysis code, which had been developed in this study, have been verified using by actual vibration test data. This fiscal year, some validation studies for the function of liquefaction analysis was conducted usig by actual measured data through the laboratory liquefaction test. (2)Supplemental Studies for JNC Second Progress Report. Through the JNC second progress report, it was considered that the stability of earthquake resistance of the engineered barrier system would be maintained under the major seismic event. At the same time we have recognized that several model parameters for joint-crack element, which takes into account for the response behavior of material discontinuous surface such as between overpack and buffer material, will become important in the response behavior of the whole EBS. This year, we have studied about several topics, which arise from technical discussion on JNC second progress report and we have discussed about total seismic stability of EBS. (3)Supplemental Studies for joint study with NRIDP. At this fiscal year, the joint study with National Research Institute for Disaster Prevention (NRIDP) will be final stage. UP to this day, incremental validation studies had been continued using by mesuared data obtained from vibration test. In this final stage, validation analysis has been conducted again using by current version new analysis code and maintained the validation data which will be contribute to the joint study mentioned above.
*; *; Morooka, Koichi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-043, 170 Pages, 2000/03
This study is an object to collect and arrange data about the mass transfer path during a natural barrier system by grasping actual rock feature, in order to be useful for a performance assessment of a natural barrier system at geological disposal of HLW. An existence of permeability high large-scale faults extends a large influence over a performance assessment of geological disposal. With "The Second Progress Report on Research and Development for the Geological Disposal of HLW in Japan" which Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) issued, it is as" A repository would be located at least 100 meters away from major faults and major fracture zones which could adversely affect the stability and performance of the repository" as a Reference Case concept model of a natural barrier system, Then, they are as "in the Reference Case, the transport path consists of the host rock and the downstream fault". It will not be easy to know the distribution of faults in the subsurface deep division without data acquired from many boreholes and underground laboratory. With this study, specific data on the large-scale faults and fracture zones has been collected and arranged by investigating in underground galleries and on the literatures of a post-operated mine site. Based on this result, a consideration on the principal transfer pass at a natural barrier system has been conducted. The contents conducted in this report is the follows. (1)investigation of literature about data of fracture, shear zone, and geology, (2)field investigation of fracture and shear zone in the rock, (3)arrangement of these results, (4)modeling of the major water conductive feature, and (5)evaluation of an assumption which has been introduced in the Second Progress Report issued by JNC.
Ikeda, Takao*; Yoshida, Hideji*; Miki, Takahito*
JNC TJ8400 2000-046, 264 Pages, 2000/02
This report contains discussions about methodology for the selection of parameter values, stochastic approach for the biosphere assessment and biosphere modelling for marine discharge case are described. Regarding the methodology for the selection of parameter values, important aspects for the data selection were discussed, and data selection protocol was developed. Regarding the stochastic approach for the biosphere assessment, it is confirmed that Straightforward Monte Carlo Method and Latin Hypercube Sampling Method are the most adequate based on a literature survey. Then stochastic assessment by using biosphere model that was developed in the second progress report was carried out to check the sensitivity of parameter values. Finally, availability of several kind of assessment models for marine discharge case were discussed. It was confirmed that Multiple Compartment Model was the most applicable. Assessment using Multiple Compartment Model was carried out. The results were compared with those derived by numerical model. As a result, the difference between two models were small enough.
*
JNC TJ8400 2000-017, 74 Pages, 2000/02
The report concerns the improvement of the method measuring thermal conductivity of buffer materials using a thermistor probe and the measurement of thermal conductivity of compacted bentonites and mixtures of bentonite and silica sand using the proposed method measuring thermophysical properties. The method measuring thermal conductivity is improved in accuracy and the apparatus is improved so as to measure easily with more short time. The calculated values of the conventional correlations predicting thermal conductivity of bentonite and mixture were compared with the exising and present data of thermal conductivity of bentonites and mixtures. The correlation proposed by Sakashita and Kumada can predict the best fitted values with the data of the bentonites and Fricke and Bruggeman correlations are fitted with the data for the mixtures with practical accuracy.
Sumiyama, Morio*
JNC TJ8400 2000-009, 138 Pages, 2000/02
To evaluate corrosion behavior of carbon steel, a candidate materials of overpack, buried in soil for a long time, the water pipes buried in freshwater clay for a long time we digged out and the soil environment and the corrosion weight loss of pipes have been researched. From the results, a corrosion model (an empirical equation), an oxygen reduction reaction rate-determing step type, of carbon steel buried in soil was introduced. The corrosion data of under ground pipe collected by the Japan Community Gas Associations was used to increase reliability of the corrosion model equation. These data are one of researches of corrosion behavior of carbon steel buried in soil for a long time studied by at home and abroad. 38 samples buried freshwater clay were selected in 171 samples. With estimating the corrosion velocities and the soil environment factors of the above data, the maximum depth of pit corrosion was calculated by the statistical method of the extreme values using the area of overpack as the recurrent time. The correlation between the soil environment factors and the corrosion weight loss was obtained by the correlation analysis. The corrosion model of the maximum depth of pit corrosion at 0.99 of cumulative probability was compared between the under ground pipe data and the above data. On the reference data and the above data, the corrosion model equation; H = aY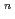 was compared with the maximum depth of pit corrosion at 0.99 cumulative probability. The data of water pipes and community gas pipes at 0.99 cumulative probability showed the reasonable values when these data were compared with the reference data. So that the model was proved as a good corrosion model m the neutral low dissolved oxygen environment.
was compared with the maximum depth of pit corrosion at 0.99 cumulative probability. The data of water pipes and community gas pipes at 0.99 cumulative probability showed the reasonable values when these data were compared with the reference data. So that the model was proved as a good corrosion model m the neutral low dissolved oxygen environment.
Imai, Jun*
JNC TJ8400 2000-008, 196 Pages, 2000/02
The objective of this research is to make clear long-term alteration processes of bentonite contacting with concrete under a repository condition for radioactive waste. The Uzu tunnel in yamagata prefecture in Japan, constructed during the term of December of 1963 to July 1967, was selected as an appropriate natural analogue: the tunnel wall was made of portland cement and which has been contacting with a bentonite bed during 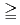 32 years. Sample analyses indicated that the original bentonite was Na
32 years. Sample analyses indicated that the original bentonite was Na -type and it changed to Ca
-type and it changed to Ca -type in the range of a few millimeters from the contact. Although a Ca
-type in the range of a few millimeters from the contact. Although a Ca leaching was also observed from the concrete near the contact, neither transformation to zeolite nor to illite was recognized. On the other hand, sulfur increased and ettringite (3CaO
leaching was also observed from the concrete near the contact, neither transformation to zeolite nor to illite was recognized. On the other hand, sulfur increased and ettringite (3CaO  Al
Al O
O
 3CaSO
3CaSO 4
4  32H
32H O) was recognized in the concrete within the depth about 30 mm from the contact.
O) was recognized in the concrete within the depth about 30 mm from the contact.
Miyake, Yasuhiro*; *; ; Kimura, Nobuyuki
JNC TN9400 2000-016, 40 Pages, 1999/12
ln the conventional visualization system for the computational results, only Japanese (Nihongo) Line Printer (NLP) was available to print two dimensional cross sectional plots of vector and scalar fields. To evaluate the phenomena, an analyst had to print many plots on the NLP. This task makes difficult to check the computational results immediately after the calculation. Recently, as the visualization tools, we introduced Micro AVS and Field View which are utilized widely in the scientific and the industrial fields. ln order to show the numerical results on the visualization software, we constructed a post processing system which convert the results of the numerical code to "lntermediate files" which can be read by the visualization tools. As using this system, the examination of the numerical results can be executed on the display of the personal computer. Furthermore, the persuasive report and paper with high quality can be produced due to the color printing. As for the transient calculation, the change of the phenomena can be visually evaluated by using the animation function.
Sawada, Atsushi; Ijiri, Yuji; *; Watari, Shingo
JNC TN8400 99-093, 58 Pages, 1999/11
This paper decribes the results of PA studies considering heterogeneous fracture characteristics, for the purpose of contributing for the performance assessment of the natural barrier system PA in H12 report (The second progress report on research and development for the Geological Disposal of HLW in Japan). In this study, 3-D discrete fracture network mode1 (DFN) and 1-D multiple pathways model is applied for 100m scale of rock block. Although nuclide release rate calculated by DFN are widely distributed among the realizations, it is shown that several tens realizations are enough number to understand the stochastic characteristics of the nuclide release. From the data uncertainty analysis, there are no significant effects for the nuclide retardation in fracture geometry parameters such as fracture radius, density and etc. 1-D multiple pathways model is developed with focusing on the heterogeneity of the transmissivity, which has a large effect to the nuclide retardation effects. The nuclide release rate calculated by using 1-D multiple pathways model approximates to the results of DFN. This result also shows that the relatively large fractures/faults that connects disposal tunnel and downstream faults have an important role for performance assessment in natural barrier system.